Goiter
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. Thyroid hormones play a role in some bodily functions, including metabolism, body temperature, mood and heart rate control….
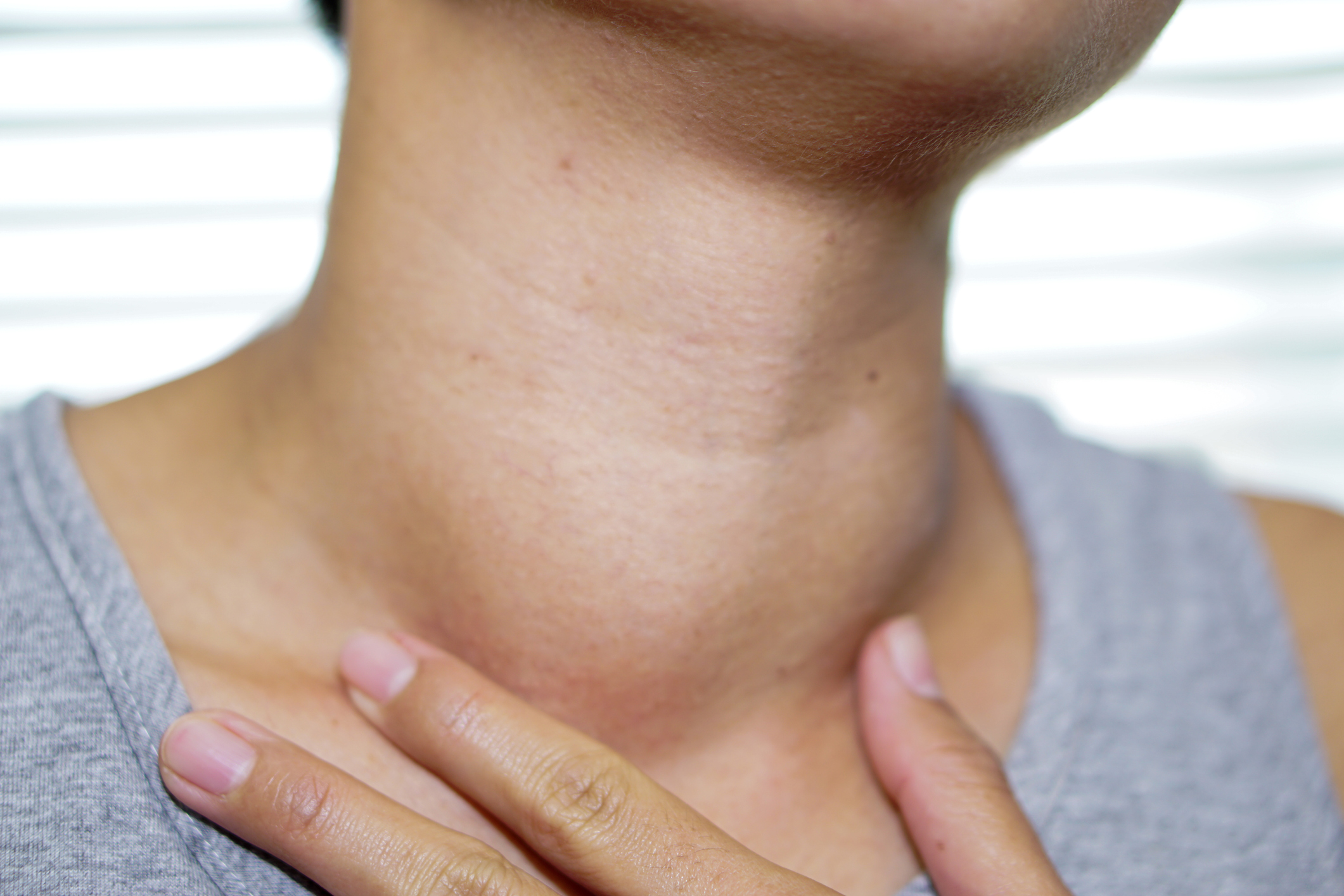
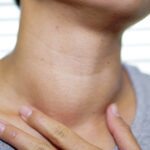
Goiter (goiter) is a condition in which the thyroid gland grows larger than normal. The entire thyroid gland can grow larger or it can develop into one or more small masses called thyroid nodules. Although goiter is usually painless , the presence of a large enlargement of the thyroid gland can cause coughing and difficulty swallowing ….
Types of goiter
Types of goiters based on how they grow and enlarge include:
1. Simple (diffuse) goiter
This type occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, and the gland grows more to make up for it.
2. Endemic goiter
Also known as a colloidal goiter, this enlargement is caused by a lack of iodine in the diet, which causes the thyroid gland to work harder to produce it.
3. Multinodular goiter
This condition occurs when nodule-shaped masses grow in the thyroid gland. This condition may be described as toxic.
3. Non-toxic goiter
Nontoxic goiter is a noncancerous enlargement that occurs when thyroid levels remain normal. The cause of nontoxic goiter is usually unknown, although it may be related to the consumption of certain medications such as lithium.
Symptoms of goiter
Most people with goiter show no signs other than swelling at the base of the neck. In many cases, the size of the goiter may be small and only appears when routine medical examinations or imaging tests are performed. The indications and symptoms that may appear in the patient depend on the following:
- A bump appears in the front of the neck
- A feeling of tightness in the throat area
- Hoarseness
- Swelling of a vein in the neck
- Dizziness when raising the arms
Other symptoms
Other less common symptoms include:
- Difficulty or shortness of breath
- cough
- beeps
Also read: Thyroid disorders: Learn about its symptoms and complications
Causes of goiter
A goiter is an adaptive reaction of thyroid cells to a process that inhibits the production of thyroid hormone. The most common cause of goiter is iodine deficiency, but many conditions can cause it, including:
1. Iodine deficiency
Iodine is a necessary element that helps the thyroid gland produce thyroid hormones. If a person does not have enough iodine in their diet, goiter can be a sign that the thyroid gland is not able to produce enough thyroid hormone. The use of iodized salt prevents iodine deficiency in the diet.
2. Graves’ disease
It is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, causing it to grow larger. The latter can cause hyperthyroidism in some cases, so it is important to treat it.
3. Hashimoto’s disease
An autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the thyroid gland. Some people with the disease develop an enlarged thyroid gland. This type of inflation usually improves on its own over time. Some cases of Hashimoto’s disease require treatment with thyroid hormones.
4. Inflammation of the thyroid gland
Thyroiditis can lead to an enlarged thyroid gland. This is due to several reasons, including the consumption of certain medications that are used to treat some mental health conditions, in addition to other medical conditions.
5. Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer often leads to thyroid diseases, including goiter.
6. Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes, especially an increase in estrogen levels during puberty, pregnancy or menopause, can trigger goiter.
7. Smoking
interferes thiocyanate Existing in tobacco smoke with the absorption of iodine, which may cause goiter.
8. Excess iodine
Excess iodine is a less common cause of goiter, however, in some cases, excessive iodine intake can lead to an enlarged thyroid gland.
How is an enlarged thyroid gland diagnosed?
Often, a goiter will be diagnosed by conducting the following tests:
physical examination
An enlarged thyroid gland is revealed by palpating the neck area for nodules and revealing the size of the gland.
blood test
A blood test detects certain antibodies, which are proteins made by white blood cells that are produced in some forms of goiter. These antibodies help protect against viruses that cause illness or infection in the body.
Thyroid function test
This test is done to check the size of the thyroid gland. Tests are performed to check the size and function of the thyroid gland, by injecting a small amount of radioactive material into a vein to produce an image of the thyroid gland on a computer screen.
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging
In this test, sound waves are sent through the tissues of the body to record the echoes and convert them into an image or video. A specialist doctor can check the size of the thyroid gland and whether it has nodules.
biopsy
During this procedure, a sample of tissue or cells is removed for laboratory study. This procedure is often used if there are large nodules in the thyroid gland, as well as to rule out cancer cases.
How do I know that I have an enlarged thyroid gland?
Goiter usually appears as a swelling or lump in the front of the neck. This swelling does not cause any pain. In some cases, the swelling is on one side of the neck.
Treatment of goiter
Treatment depends on the size and growth of the thyroid gland and its causes. Treatment methods are divided into the following:
1. Pharmacotherapy
In most cases, medications for hypo or hyperthyroidism may be sufficient to reduce the size of the thyroid gland. In some cases, aspirin or corticosteroids are used to treat goiter caused by inflammation.
2. Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is used if the swelling is very large or when the person does not respond to drug treatment, or when the tumor becomes cancerous, then the entire thyroid gland must be surgically removed. After this, the patient may need to take thyroid hormone medication for life.
3. Other treatments
Radioactive iodine treatment
This type of treatment involves taking radioactive iodine by mouth. Where iodine goes to the thyroid gland and kills its cells, causing it to shrink. After radioactive iodine treatment, you’ll likely need to take thyroid hormone replacement therapy for the rest of your life. This treatment is used in cases of hyperthyroidism.
Tips for living with goiter
If the goitre is caused by iodine deficiency, an iodine diet can be followed, including crustacean fish, salty sea fish, seaweed, milk derivatives, eggs, soy products…, and table salt that contains iodine.
It should be noted that the recommended daily amount of iodine does not exceed 150 micrograms. As an excess of iodine in the diet can cause thyroid gland dysfunction. In cases that require medical treatment, it is necessary to adhere to the medication.
Frequently asked questions that may interest you
How long does it take to treat goiter?
The swelling usually disappears after the start of treatment. In cases where the size of the swelling increases, it is important to consult a doctor.
When is goiter dangerous?
Goiter is not often dangerous, but the latter may obstruct the airway and larynx if it is large. Changes in the process of secretion of thyroid hormones associated with goiter can also cause complications for the body.
The thyroid gland may stop producing enough hormones. This condition is called hypothyroidism. In some cases, the swelling of the thyroid gland becomes toxic. Goitre is dangerous if the underlying cause of the goiter is thyroid cancer. It is important to determine the cause of goiter to rule out cancer cases.
Also read: When does the doctor resort to thyroidectomy?